What is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity refers to the practice of protecting computers, networks, systems, and data from digital threats, such as cyberattacks, hacking, data breaches, malware, and other forms of unauthorized access or damage. It involves a combination of technologies, processes, and best practices to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information.
Network Security
Network security involves protecting the integrity of networks and data during transmission. It focuses on defending against unauthorized access, misuse, or attacks on computer systems and networks.
Information Security
Information security is the practice of safeguarding the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information, whether it's stored digitally or physically.
Application Security
Application security focuses on protecting software applications from vulnerabilities and exploits that could be used by attackers to gain unauthorized access or cause damage.
Incident Response
Incident response is the process of detecting, responding to, and recovering from a security breach or cyberattack.
Disaster Recovery
Disaster recovery focuses on preparing for and recovering from significant events that cause data loss, corruption, or system downtime, such as cyberattacks, natural disasters, or technical failures.
Endpoint Security
Endpoint security involves securing individual devices (endpoints) such as computers, smartphones, tablets, and other devices that connect to the network.
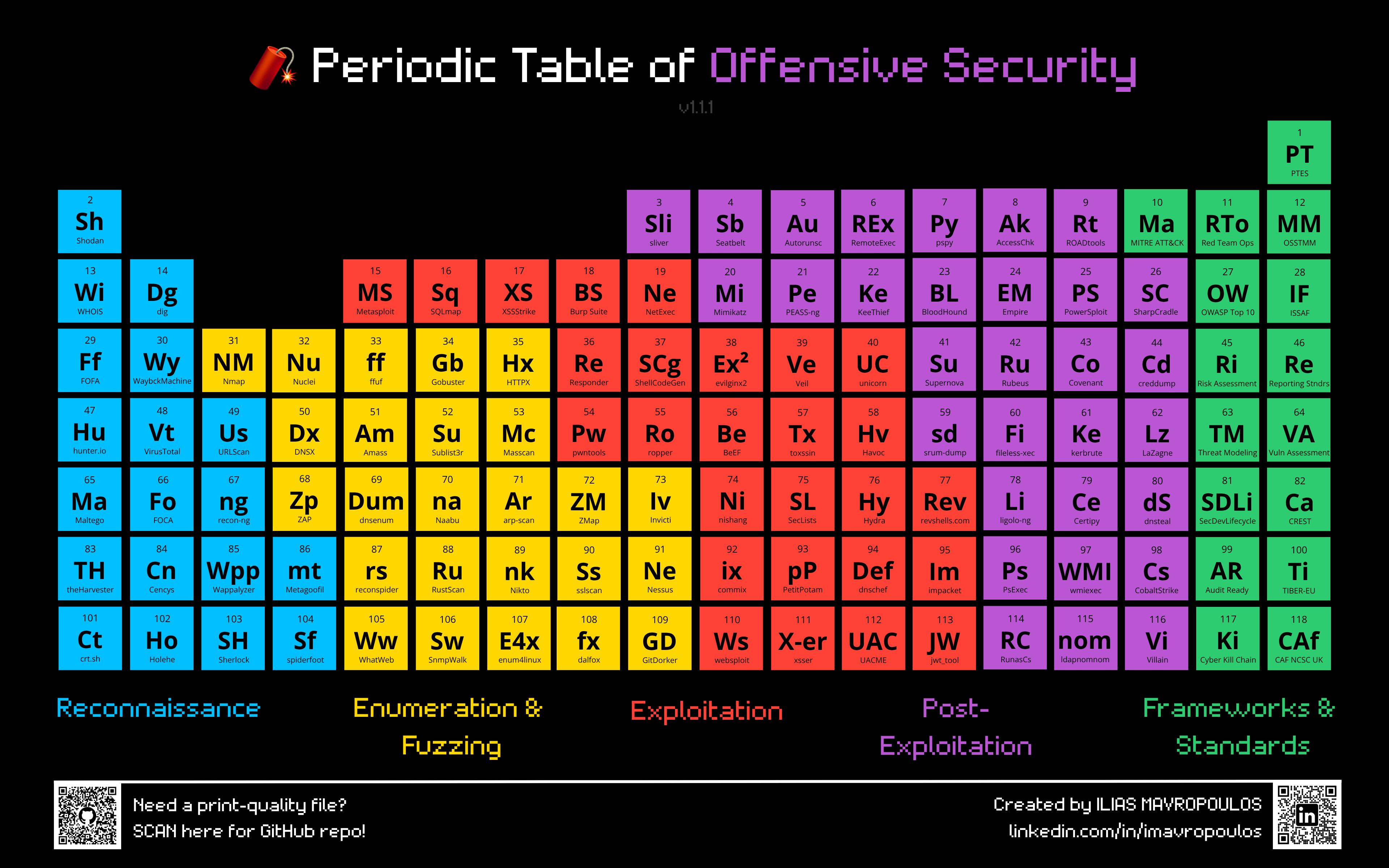
Periodic Table of Offensive Security
A visual reference of 118 essential tools, frameworks, and standards used in offensive security and red teaming, organized like a periodic table.
What is CVEs?
CVE (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures) is a standardized system for identifying and cataloging publicly disclosed cybersecurity vulnerabilities. It is maintained by MITRE Corporation with funding from the U.S. Department of Homeland Security (DHS). Each vulnerability is assigned a unique CVE ID to ensure that security professionals refer to the same issue consistently across different platforms and tools.
Buffer Overflow
Occurs when more data is written to a buffer than it can hold. Can lead to crashes, arbitrary code execution, and security breaches.
Injection Attacks
Includes SQL Injection (SQLi), Command Injection, and Code Injection. Attackers insert malicious code into an application to manipulate or steal data.
Security Misconfigurations
Happens when applications or systems have weak security settings. Examples: Default passwords, open cloud storage, and excessive permissions.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
A web vulnerability where attackers inject malicious scripts into web pages. Affects users by stealing session cookies, redirecting to malicious sites, etc.
Denial-of-Service (DoS)
Overloads a system, making it unavailable for legitimate users. DDoS attacks use multiple systems to attack a target at once.
Privilege Escalation
Attackers exploit vulnerabilities to gain higher-level access to systems. Can be Vertical (admin-level access) or Horizontal (user-level access to other accounts).
What is CVSS?
CVSS (Common Vulnerability Scoring System) is a framework used to assess the severity of security vulnerabilities. It provides a numerical score from 0.0 to 10.0, with higher scores indicating more severe vulnerabilities.
What is CPE?
CPE (Common Platform Enumeration) is a structured naming system for IT products, software, and hardware. It is used to uniquely identify products in security databases and vulnerability management systems.